Gitlab Shell Runner 环境问题解决思路
问题
GitLab Shell Runner 虽然使用方便,但在实际运行过程中可能会遇到一些环境方面的问题,比如:
- 当前 Runner 是以哪个用户身份执行的任务?我应该在哪个用户目录下安装所需的软件包?
- 为什么在 gitlab-runner 用户目录下安装的软件,在 CI 流程中却无法正常生效?
- 为什么 CI 实际运行的 Node.js 版本与我在配置中指定的不一致?
方案
仔细梳理 GitLab Runner 的工作流程,这些问题就能迎刃而解。
运行机制
Gitlab Runner 配置
Gitlab Runner 安装后以系统 Service 的方式运行,查看 Service 状态:
1 | admin@connector-backup:~$ sudo systemctl status gitlab-runner |
提取几个因素
Service 文件位置:
/etc/systemd/system/gitlab-runner.serviceService 启动命令:
/usr/bin/gitlab-runner run --working-directory /home/gitlab-runner --config /etc/gitlab-runner/config.toml --service gitlab-runner --user gitlab-runner进而看到
gitlab-runner 的工作目录为:
/home/gitlab-runner,这意味着执行 CI 时的文件下载等操作会在这个目录下进行。gitlab-runner 执行 Shell 脚本的用户是:
gitlab-runner。gitlab-runner 配置文件是:
/etc/gitlab-runner/config.toml。其配置一般如下1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18# 并发度,即同时支持多少个 runner 运行。一定得大于 1,不然会出现经常 pending 的现象。
concurrent = 5
check_interval = 0
# 单个 runner 超时时间
[session_server]
session_timeout = 1800
[[runners]]
name = "connector-backup"
url = "https://git.mampod.work/"
token = "dJd2EcP2S7dtxjrRCA2L"
executor = "shell"
[runners.custom_build_dir]
[runners.cache]
[runners.cache.s3]
[runners.cache.gcs]
[runners.cache.azure]
Shell Runner 的运行方式
根据手册。类 Unix 操作系统中,默认使用 bash,找不到 bash 时使用 sh。
Shell Runner 执行
.gitlab-ci.yml文件脚本的方式如下1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9This command is used if the build should be executed in context of another user (the shell executor)
cat generated-bash-script | su --shell /bin/bash --login user
This command is used if the build should be executed using the current user, but in a login environment
对我们来说,生效的一般是这个
cat generated-bash-script | /bin/bash --login
This command is used if the build should be executed in a Docker environment
cat generated-bash-script | /bin/bash尽管 手册 上说
.bashrc、.bash_logout等配置文件能够被加载,但实际有观察到无法被加载的情况。因此有必要研究一下 bash 加载配置文件的机制。
Bash 配置文件的加载方式
bash 有多种启动方式,不同的方式对应不同加载行为。
登录式与非登录式
- 登录式:通过 SSH、图形界面等形式启动的 bash 自动就是登录式 shell;添加
--login参数的也是。 - 非登录式:直接从命令行启动如
su another-user或bash xxx都是非登录式。
交互式与非交互式
- 交互式:顾名思义,交互式 bash 的输入输出一般连接到用户的 terminal。SSH 登录得到的 shell 是交互式的;直接
bash命令进入的 shell 也是交互式;执行单条命令时,也可以添加-i参数强制以交互式 shell 的方式执行。 - 非交互式:bash 后直接添加命令文本即非交互式。比如
bash -c 'echo hello'。
交互式 bash 多了很多行为。具体参考手册的这里。
配置加载方式一(交互式登录 shell 或者 带 –login 的非交互式 shell)
进入 shell 时
- 首先读取
/etc/profile - 然后按顺序查找
~/.bash_profile,~/.bash_login,~/.profile,读取第一个找到的文件。 - 如果 bash 参数有
--noprofile,则上述两个步骤不会执行
退出 shell 时
- 读取
~/.bash_logout(如果存在)
交互式登录 shell 中不会主动加载 ~/.bashrc ,需要在 ~/.bash_profile 等文件中手动指定:
1 | if [ -f ~/.bashrc ]; then . ~/.bashrc; fi |
配置加载方式二(交互式非登录 shell)
- 读取
~/.bashrc(如果存在) - 如果 bash 参数才有
--norc,则上述步骤不会执行
配置加载方式三 (非交互式 shell)
- 如果
BASH_ENV环境变量存在,则加载它指定的文件。否则啥都不干。
常见 bash 行为的类型
我们在 /etc/profile、~/.bash_profile、~/.bashrc 中都加入输出语句,并且 ~/.bash_profile 不主动调用 ~/.bashrc,以验证我们对配置加载的推测
SSH 登录的 shell
交互式登录 shell,走加载方式一
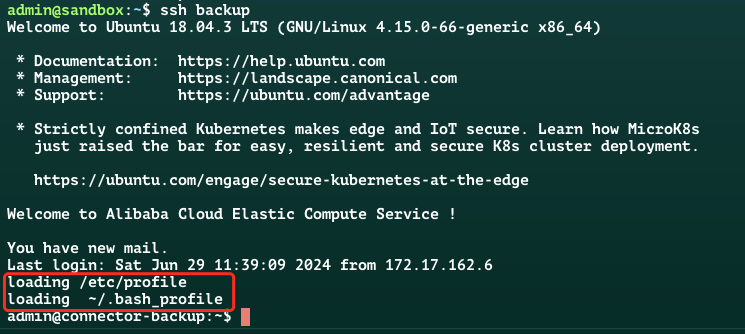
可以看到没有加载
~/.bashrcsu 到某个用户得到的 shell
交互式非登录 shell,走加载方式二
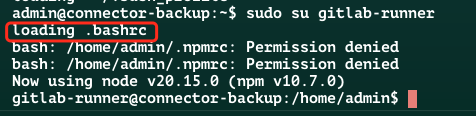
可以看到只加载了
~/.bashrc,没有加载/etc/profile、~/.bash_profilebash –login 启动的 shell
非交互式登录 shell,走加载方式一
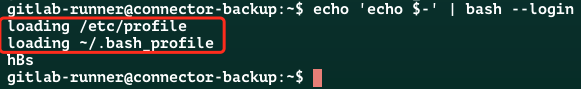
可以看到没有加载
~/.bashrcbash 启动的 shell
非交互式非登录 shell,走加载方式三
可以看到一个文件都没有加载
为何要区分登录式、交互式?
bash 的使用场景太多了,需要区分场景执行不同的行为。如,用户登录时,xxprofile 文件就应该执行以准备一些环境,并且支持登出时在 ~/.bash_logout 处理一些事务;而一般的使用 bash 命令启动的 shell,则无需进行这些操作,于是区分登录和非登录;在启动交互式 shell 时,需要设置 PS1、PS2等变量,而这在直接执行的 bash 脚本中是不需要的,于是区分交互式与非交互式。
再看问题
有了上述前置知识,再来看问题就很简单了。
当前 runner 时哪个用户在运行?
- 方式一:去 gitlab-runner.service 文件查看启动参数 –user
- 方式二:
whoami
为什么我安装的软件没有生效?
- 确定软件安装的位置,以及该位置处于 runner 运行用户的
PATH中 - 设置
PATH的位置放在~/.bash_profile中,如果放在~/.bashrc,要在~/.bash_profile加载时手动加载。
一些排查 tips
查看当前 shell 是否是登录式 shell ?
执行
echo $0- 如果输出以
-开头,例如-bash,则表示当前 shell 是登录式 shell。 - 如果输出不以
-开头,例如bash,则表示当前 shell 是非登录式 shell。
- 如果输出以
查看当前 shell 是否是交互式 shell?
官方手册提供的两种方式,
echo $-结果中带 i 的;或者存在echo $PS1存在的。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10case "$-" in
*i*) echo This shell is interactive ;;
*) echo This shell is not interactive ;;
esac
if [ -z "$PS1" ]; then
echo This shell is not interactive
else
echo This shell is interactive
fi查看当前 shell 是 bash 还是 sh?
还是
echo $01
2
3
4
5
6
7
8echo 'echo $0' | sh
sh
echo 'echo $0' | bash
bash
echo 'echo $0' | zsh
zsh验证是否加载了指定配置文件?
在配置文件中输出一段字符串,CI 中能打印出来。